Emission control
The reduction of emissions of local pollutants (NOX, CO, aldehydes, particulate matter, etc.) arising from combustion engines, industrial plants, and residential sources is achieved by advanced exhaust-gas after-treatment systems. A special focus is given to the reduction of NOX emissions by selective catalytic reduction (SCR), the elimination of toxic pollutants such as formaldehyde and HCN, and better reaction engineering strategies for the removal of the green-house gases such as CH4 and N2O. Advanced capillary techniques and laser spectroscopy such as PLIF supports the understanding of the catalytic devices for cleaning exhaust gases. Slip of the greenhouse gases methane and N2O from modern engines fueled by natural gas and hydrogen, resp., are reduced by the application of advanced catalysts and optimised operating conditions.
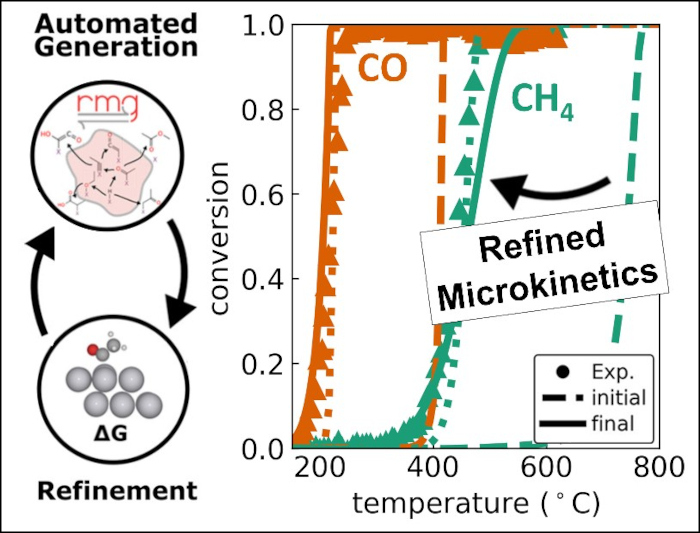
Heterogeneous catalysts based on supported noble metal clusters and particles are essential components that play a key role in numerous industrial applications such as emission control, ...
more information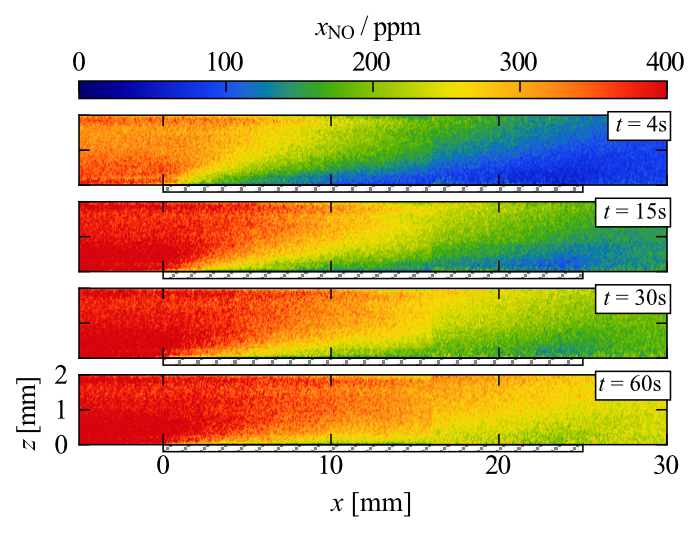
The performance of catalysts depends equally on: (1) the atomic surface structure or the structure of the molecular units, as they determine the physical and chemical and thus the catalytic properties. (2) The meso and macro scale ...
more information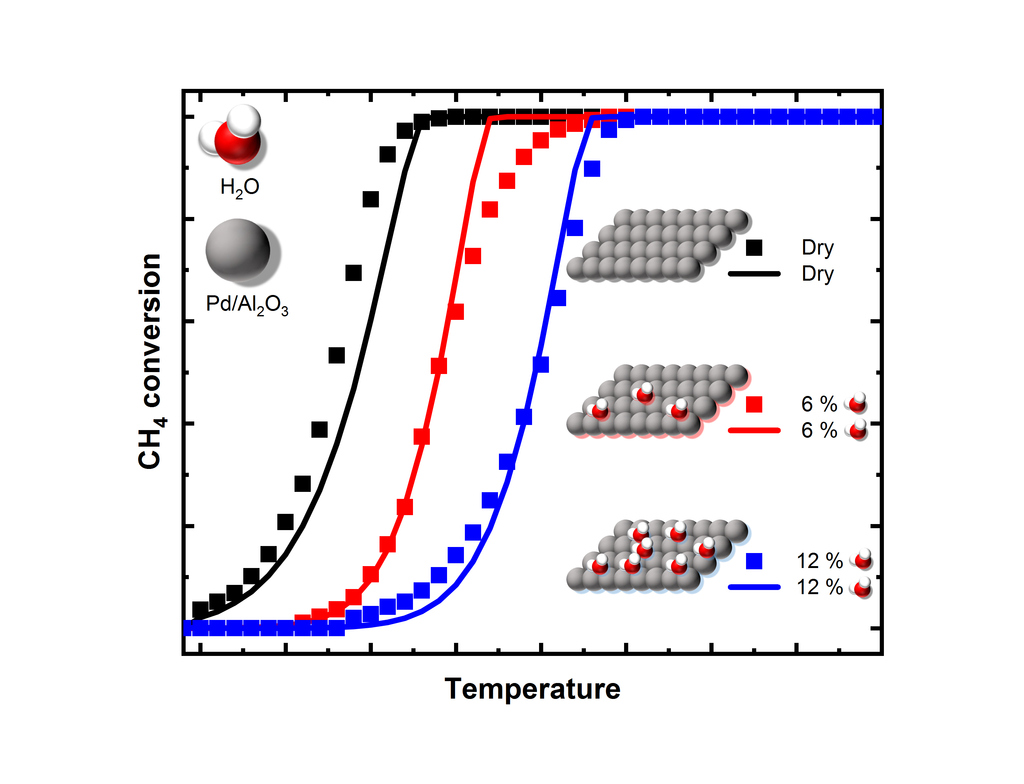
Lean-burn natural gas engines, with their high efficiency and low emissions, are a promising alternative to traditional diesel or gasoline engines. However, they emit small amounts ...
more information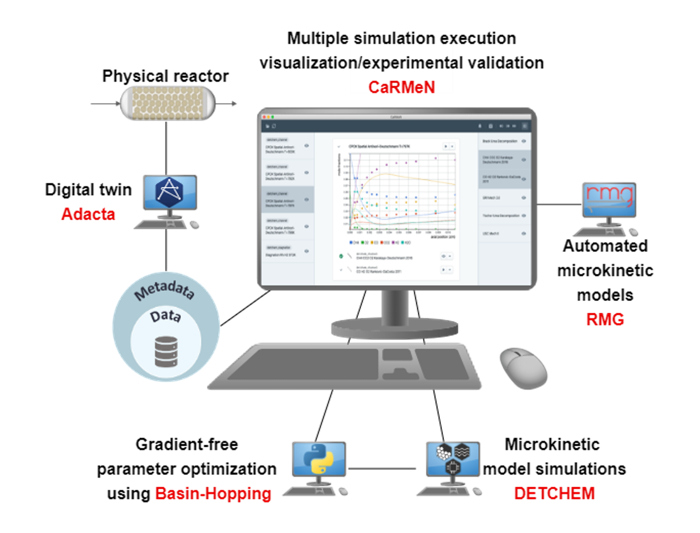
Research data management (RDM) in scientific research is crucial for ensuring the accessibility, reproducibility and reusability of scientific data. Effective RDM involves ...
more information
Compared to conventional internal combustion engines (ICE), hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) consume up to 49% less fuel under urban driving conditions and ...
more information
On the way towards sustainability, climate-friendly hydrogen-fueled internal combustion engines allow to decarbonize applications that cannot rely on electrification...
more information
Modeling and numerical simulation of multiphase chemical reactions in complex application areas are among the greatest challenges of our time. Through precise predictions ...
more informationThree-way catalytic converters (TWCs) are the main technology for the reduction of tail-gas emissions in gasoline driven vehicles. Ever since their commercial market launch in the 1970s TWCs have become the most abundant technical catalytic reactors. ...
more informationDue to limited fossil fuel resources and the necessity of reducing CO2 emissions, fuel efficient diesel and lean burn engines gain in importance. However, under these operation conditions, the abatement of NOx emissions is a challenge to exhaust gas after-treatment. ...
more informationThe optimization of technical systems in emission control is a challenging task. Due to interactions of multiphase chemical reactive flows with solid walls, problems arise for the whole system. ...
more informationTo meet the increasingly stringent emission standards, diesel vehicles currently mainly use a urea SCR (selective catalytic reduction) system for reduction of nitric oxides (NOx). The precursor of the reducing agent is dosed into the exhaust pipe ...
more informationThe project covers different aspects and models for the CFD simulation of AdBlue injection, droplet/wall interaction and deposit formation. The first research goal is the understanding of droplet/wall interaction on smooth, rough and porous surface ...
more informationSince previous investigations have shown, that the preparation of AdBlue at the beginning of the SCR catalyst is not completed and distances between injection and catalyst inlet are shortened technologically, further investigations will ...
more informationThe selective catalytic reduction (SCR) is an important technique to reduce NOx-emissions in the exhaust gas of diesel-powered engines. Ammonia is used as reducing agent, which is carried in the vehicle in form of an 32 wt- % urea water solution. ...
more informationBased on legislation for diesel engines a further minimization of emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) is essential. The selective catalytic reduction (SCR) is therefore an efficient and widely used method to reduce nitric oxide emissions, frequently in combination with other emission control devices. ...
more information
